Search Results for: equilibrium constant
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Equilibrium constant
Definition noun The ratio in which the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the... Read More
Dissociation constant
Definition noun (1) A mathematical constant that describes the tendency of a large molecule to dissociate reversibly into... Read More
Dynamic equilibrium
Definition noun A system in a steady state since forward reaction and backward reaction occur at the same... Read More
Secular equilibrium
secular equilibrium A type of radioactive equilibrium in which the half-life of the precursor (parent) radioisotope is so... Read More
Genetic equilibrium
Definition noun A condition where a gene pool is not changing in frequency because the evolutionary forces acting upon the... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. WrightDepartment of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo MinnsSubmitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009.Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Association constant
Definition noun A mathematical constant that describes the bonding affinity between two molecules at... Read More
Homeostatic equilibrium
Definition noun (1) The tendency of an organism or a cell to regulate its internal conditions, usually by a system of... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
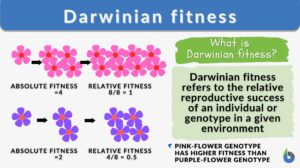
Darwinian fitness
Darwinian Fitness Definition Darwinian fitness refers to the measure of an individual organism's or genotype's reproductive... Read More
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
Definition noun A principle stating that both allele and genotype frequencies in a randomly-mating population remain... Read More
Hardy-Weinberg law
Definition noun A principle stating that both allele and genotype frequencies in a randomly-mating population remain... Read More
Mass-action ratio
Mass-action ratio The ratio of the product of all of the product concentrations divided by the product of all of the... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Hardy-Weinberg principle
Definition noun A principle stating that both allele and genotype frequencies in a randomly-mating population remain... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
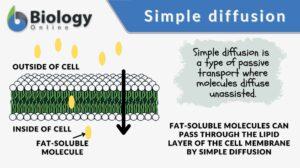
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More